The hidden danger behind shift work: kidney diseases are on the rise
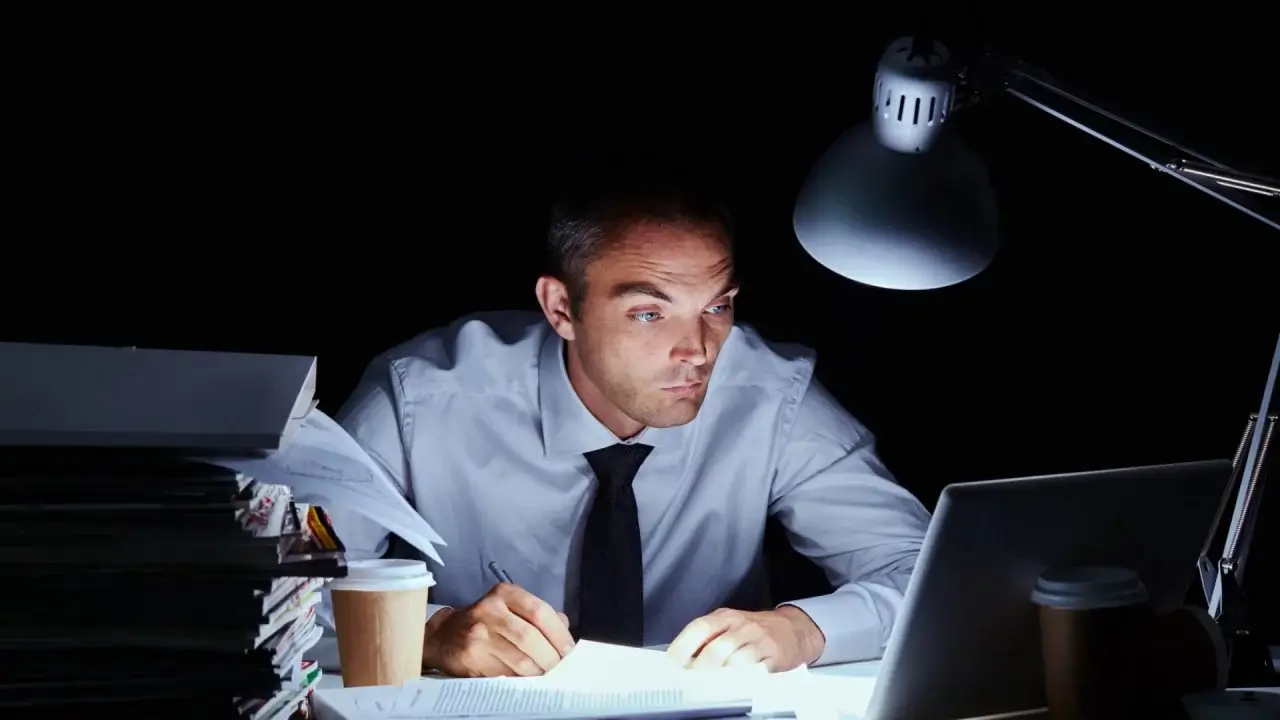

At the pace of modern life, shift work has become commonplace for many people. Some earn a stable income for their families by working around the clock, while others have the opportunity to allocate time differently in exchange for an unusual schedule. At first glance, this seems like a convenient and effective solution. However, recent research by scientists shows that serious health risks are hidden behind this.
Specialists from Sun Yat-sen University studied data from more than 220,000 people who participated in the British Biobank project. The findings were published in the prestigious Mayo Clinic Proceedings (MCP). According to them, those who work at night or at an unusual time have an average of 15 percent higher chance of developing kidney stone disease. The most dangerous aspect is that this condition is especially observed in young people and those engaged in low-intensity work.
Main causes of risk
Scientists attribute this situation to several factors. First of all, the shift worker often consumes fast food, salty and fatty products. This leads to an increase in minerals in the urine, and over time, they turn into stones.
The second serious reason is not drinking enough water. When the body is left without fluid, salts crystallize faster in the ureters, and the load on the kidneys increases even more.
Lack of physical activity and smoking habits also exacerbate the situation. An inactive lifestyle disrupts metabolism and negatively affects kidney function.
The biggest problem is sleep disorders. Working at night changes a person's biological clock, disrupts hormonal balance, and as a result, disruptions in metabolism occur.
What measures can be taken?
Experts say that it is difficult to completely eliminate this risk, but it can be reduced. To do this:
- Drinking enough water,
- restriction of salt and fatty foods,
- making short walks at each break,
- it is important to improve sleep quality and quit smoking.
Interesting conclusion of scientists
The most interesting aspect of the study is that those who worked shifts for many years have a slightly lower risk of stone formation. This is explained by the "healthy worker effect": that is, only a healthy person can withstand a heavy regime. At the same time, it is possible that over time the body will partially adapt to working at night. However, the full mechanism of this process has not yet been studied.
Conclusion
The negative impact of shift work is obvious and undeniable. However, both employers and workers must take steps to mitigate its damage. It is necessary to establish healthy eating corners, sports facilities, and regular medical examinations at enterprises. Workers, in turn, should pay attention to drinking water, maintaining moderate weight, and choosing an active lifestyle.
Read “Zamin” on Telegram!