New way to treat bone loss: scientists create effective hydrogel
Osteoporosis develops when the balance between osteoblasts (cells that form bone tissue) and osteoclasts (cells that break down bone) is disrupted in the human body. Osteoclasts change the structure of the skeleton and strengthen it, but if their number exceeds osteoblasts, bone tissue gradually disappears and the bones become brittle.
Currently, drugs are used to treat osteoporosis, either slowing down the destruction of old bone tissue or stimulating the formation of new tissue. However, the effects of these drugs begin to be felt after 12 months, during which time the patient is at risk of serious injury. The drugs can also have side effects and may not be effective at all in some patients.
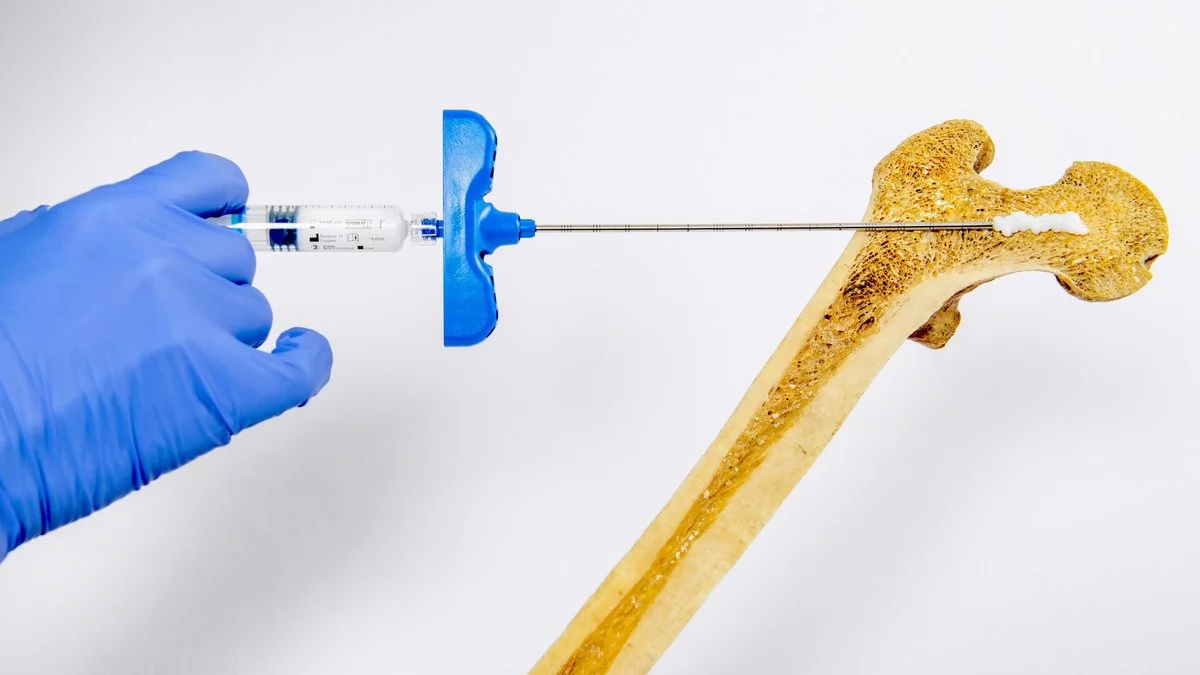
To solve the problem, scientists at the EPFL University in Switzerland have developed an innovative hydrogel, writes New Atlas. The substance contains hyaluronic acid (a substance produced by the body's connective tissues) and hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (the main building block of liquid tissue).
Laboratory tests were conducted on rats. When the hydrogel was injected into animals with osteoporosis, bone density increased by 2-3 times within 2-4 weeks. Another group of rats first received standard hormonal treatment, and then they were injected with a hydrogel mixed with a drug that slows the development of osteoporosis. As a result, their bone density increased by 4.8 times.
Although some of the side effects of hormonal treatments may persist, the new method is more effective in a shorter period of time. If the hydrogel is approved by the relevant regulatory authorities, the scientists plan to test it in humans. Read “Zamin” on Telegram!
Ctrl
Enter
Found a mistake?
Select the phrase and press Ctrl+Enter 





















